The Ketogenic Shift: From Fat to Fuel
In a world where carbohydrates have long been the primary source of energy, the ketogenic diet introduces a transformative approach: utilizing fat as the main fuel. This shift not only redefines dietary habits but also offers potential benefits for weight management, mental clarity, and overall health.
Understanding the Ketogenic Diet
The ketogenic diet is a high-fat, moderate-protein, and low-carbohydrate eating plan designed to induce a metabolic state known as ketosis. In ketosis, the body shifts from relying on glucose derived from carbohydrates to burning fat for energy, producing molecules called ketones in the process .Verywell Health
The Science Behind the Shift
Under typical dietary conditions, carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, which serves as the body's primary energy source. However, when carbohydrate intake is significantly reduced, the body's glucose reserves deplete, prompting the liver to convert stored fat into ketones. These ketones then become the alternative energy source for various bodily functions KetoLiving.
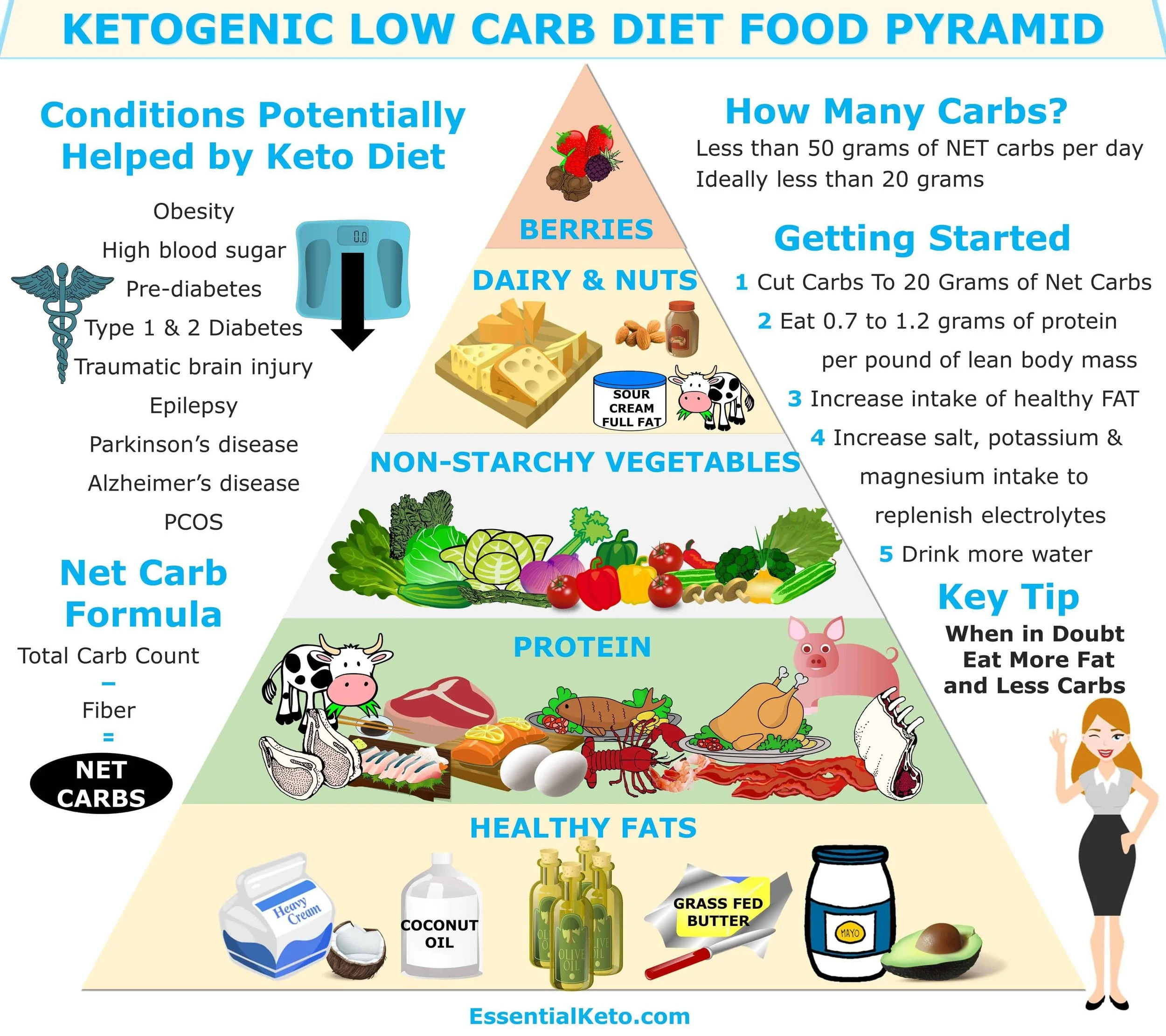
image courtesy of EssentialKeton.com
Benefits of Fat as Fuel
1. Weight Management: By tapping into fat stores for energy, the ketogenic diet can lead to significant weight loss. This approach not only reduces fat mass but also helps in preserving lean muscle tissue
2. Enhanced Mental Clarity: Ketones are a more efficient fuel for the brain compared to glucose. Many individuals on a ketogenic diet report improved focus, reduced brain fog, and heightened cognitive function.
3. Stabilized Blood Sugar Levels: With minimal carbohydrate intake, blood sugar levels remain more consistent, reducing the risk of insulin spikes and crashes. This stability can be particularly beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes .
4. Increased Energy Levels: Once adapted, the body efficiently burns fat for energy, leading to sustained energy levels throughout the day without the typical highs and lows associated with carbohydrate consumption.
Achieving and Maintaining Ketosis
To enter and sustain ketosis:
Limit Carbohydrates: Consume between 20-50 grams of net carbohydrates per day.
Increase Healthy Fats: Fats should constitute about 70-80% of daily caloric intake.
Moderate Protein Intake: Protein should make up 10-20% of daily calories to prevent gluconeogenesis, where excess protein is converted into glucose.
Stay Hydrated: Adequate water intake supports metabolic processes and helps mitigate symptoms like the "keto flu."
Monitor Ketone Levels: Regular testing can help track progress and ensure the body remains in ketosis.
Potential Challenges and Considerations
While the ketogenic diet offers numerous benefits, it's essential to be aware of potential challenges:
Keto Flu: As the body adjusts, some may experience symptoms like fatigue, headaches, and irritability.
Nutrient Deficiencies: Restricting certain food groups can lead to deficiencies in vitamins and minerals. Incorporating a variety of low-carb vegetables and considering supplementation can help.
Digestive Issues: Changes in fiber intake may affect digestion. Ensuring adequate fiber from non-starchy vegetables is crucial.
Sustainability: The restrictive nature of the diet can be challenging for long-term adherence. Planning and variety are key to maintaining the diet.
Conclusion
The ketogenic shift from carbohydrate reliance to fat utilization marks a significant transformation in dietary approaches. By understanding the science behind ketosis and being mindful of the diet's requirements and challenges, individuals can harness the potential benefits of this metabolic state. As with any dietary change, it's advisable to consult with healthcare professionals to ensure it aligns with individual health needs and goals.